Air Leak Test System For Packaging Containers
Air Leak Test System For Packaging Containers
This product is one that complies with Japanese laws and is intended for use within Japan.


Inspection target examples.
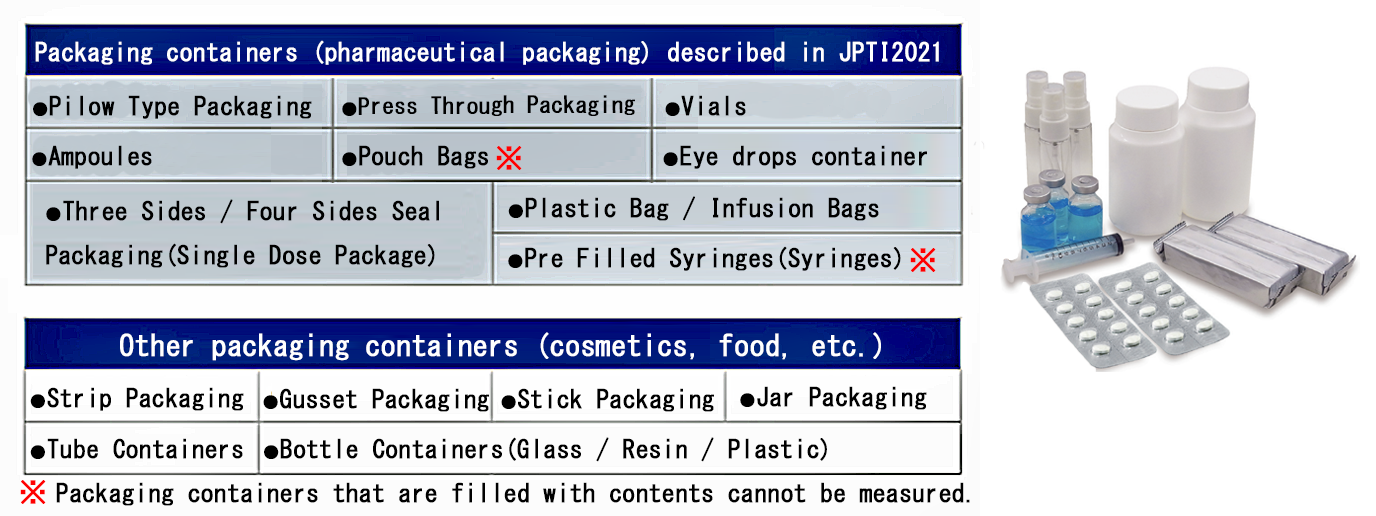
Pharmacopoeia and CCIT (Container Closure Integrity Test :CCIT)
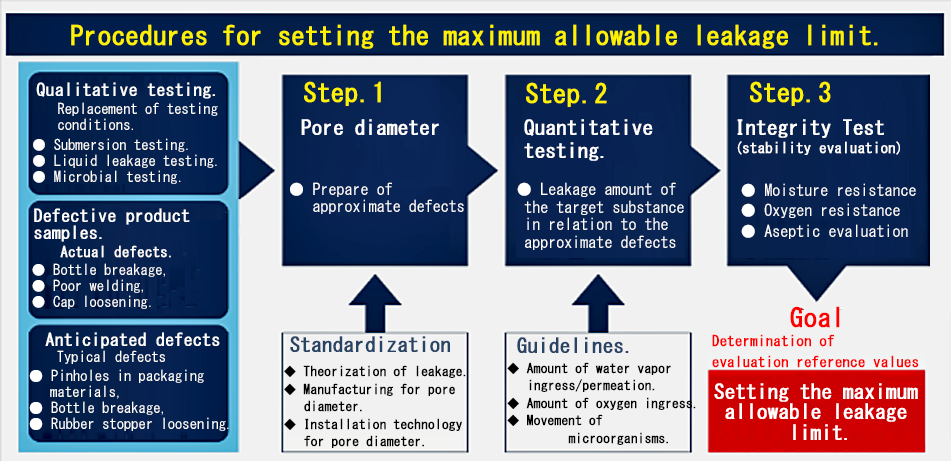
Japanese Pharmacopoeial Inclusion of CCIT and Establishment of Theory
n June 2021, the eighteenth revision of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia included reference information on "Integrity Test of Aseptic Pharmaceutical Packaging and Container Closure Integrity Test Methods," explicitly detailing 11 types of qualitative and quantitative Container Closure Integrity Test methods. Similar to USP <1207>, it became necessary to quantify and qualify using "Maximum Acceptable Leakage Limits." This means that from the perspective of quality assurance, it has become essential to determine the acceptable limits of leakage for each pharmaceutical package and to manage it quantitatively to remain below the acceptable value, establishing a significant premise for the completeness evaluation of pharmaceutical packaging.
In this revision, it was shown that the key "Maximum Acceptable Leakage Limits" correspond to the size of leakage pathways (pores) during packaging design and formulation design; however, specific methods for setting these limits were not provided. At FUKUDA, we have been collaborating with stakeholders from academia, industry, and government to compile the theories and procedures that serve as the foundation for completeness evaluations in line with USP guidelines, and we have been advancing the systematization of judgment criteria and setting procedures. To realize quality control based on the "Maximum Acceptable Leakage Limits," we are concretizing implementation methods, such as the development of Container Closure Integrity Testing equipment and the establishment of leakage testing methods using simulated defects.
Container Closure Integrity Testing (CCIT) of Pharmaceutical Packaging
Pharmaceutical packaging protects the formulation from the intrusion of water vapor, oxygen, and microorganisms throughout its shelf life, ensuring packaging integrity through the implementation of quantitative leakage testing based on the 'Maximum Acceptable Leakage Limits.' JP18 and USP <1207> recommend the use of positive controls (defective samples) and negative controls (good samples) for the evaluation as a requirement for integrity assessment.
Manufacturing Process Management and Quality Assurance.
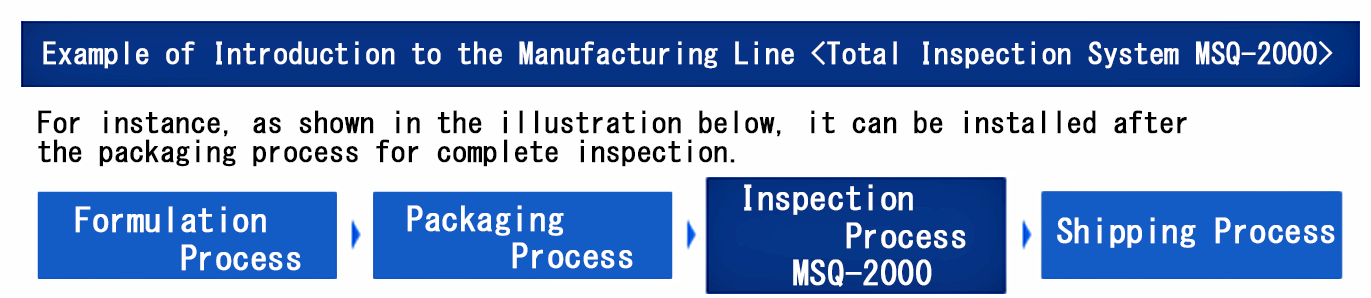
Introduction of Manufacturing Process Management (Leakage Testing Equipment)
The leakage testing equipment can fully automate the leakage inspection process on the production line. Based on predetermined quality standards, it ejects defective packaging containers. The measurement data is output in a protected form, leaving an inspection trace (log) to prevent tampering.
Quality Assurance (Protecting Pharmaceuticals Throughout the Shelf Life of the Formulation)
・Elimination of defective packaging containers (such as pinholes, improper sealing, etc.)
・Optimization of processes (optimizing conditions of packaging machinery, confirmation using positive controls)
・Verification of airtightness and seal integrity to protect manufacturers from losses due to recalls, lawsuits, and potential defects.
Measurement Principles of Air Leak Testing.
Measurement Method
The leak testing of packaging containers is conducted by comparing the pressure change values of good and defective products. The measurement methods include tank pressurization and tank differential pressure, which are selected based on the type, shape, and testing conditions of the packaging container. To perform optimal leak testing, it is necessary to confirm the shape, volume, and test pressure of the packaging containers to be inspected through preliminary validation experiments. The operations of each measurement method can be viewed in the animation below. Here, the flow of air is indicated by color, and the measurement actions for good and defective products are demonstrated using a vial bottle as an example. The sample is placed in the chamber, and pressure is either increased or decreased to detect leaks based on the pressure changes within the chamber. If there is a defect in the sample, air will move between the inside and outside of the packaging container, indicating a leak. The measurement time is approximately 20 seconds in total. If you have any questions regarding the measurement principles or testing conditions, please feel free to contact us.

Circuit Operation (Animation)
・The animation plays in the order of <Good Product → Defective Product (Small Leak) → Defective Product (Large Leak)>.
・It summarizes the operations for both positive and negative pressure.
・The animation duration differs from the actual measurement time."
・Japanese display